Below is a Fischer projection of D-glucose in its open chain form. Draw the Fischer projections for D-glucose and D-ribose.
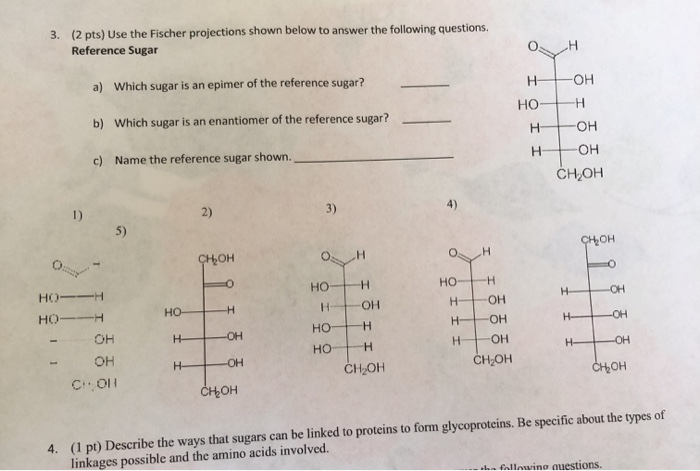
Solved 3 2 Pts Use The Fischer Projections Shown Below To Chegg Com
The sugar is ketohexose and is a D enantiomer and has 3 chiral centre and has 8.
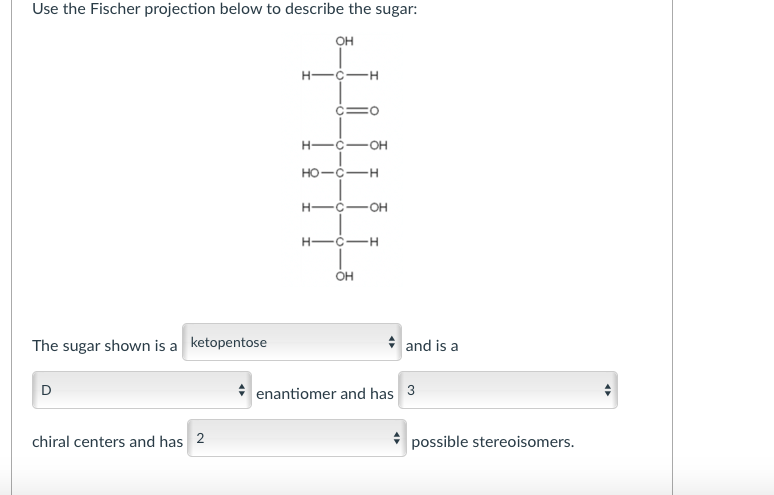
. Has an upward projection in a Haworth projection. Given a Fischer projectionof a monosaccharide identify it as a D-sugaror L-sugar. Are these two carbohydrates enantiomers.
E None of the answers is correct. If the hydroxyl group or amino group for amino acids is pointing to the left in the Fischer projection the sugar or amino acid is designated as L. 3- triose 4- tetrose 5- pentose 6- hexose 2 CH2OH groups on a cyclic means it is a ketose if 1 CH2OH group is present it is an aldose keto or aldo.
Has a downward projection in a Haworth projection. Is mannose a D-sugar or an L-sugar. If the hydroxyl group or amino group for amino acids is pointing to the right in the Fischer Projection the sugar or amino acid is designated as D.
May be either up or down in a Haworth projection it depends on the individual sugar. The sugar residue 1 from left has C2C3C4 C5 chiral. Is missing from a Haworth projection.
Below are three representations of the open chain form of D-glucose. Which of the following could be the correct Fischer projection for glucose which has a molecular formula. Glucose is mainly manufactured by plants and most of the algae during the process of photosynthesis.
Select the answer with the correct explanation below. Below are two different representations of R-glyceraldehyde the smallest sugar molecule also called D-glyceraldehyde in the stereochemical nomenclature used for sugars. Choose either one and sketch it as it would appear if it was an L-sugar.
It is a simple sugar having a molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. Use a Fischer projection to describe the stereochemistry of meso-tartaric acid by dragging the hydrogens and hydroxyl groups to the appropriate boxes in the figure below. Total 13 carbons are chiral cThe covalent bond between two sugar moeities as a result of a condensation reaction is known as Glycosidic linkage.
In the conventional Fischer projection A in the line structure variation of the Fischer projection. Below are two different representations of R-glyceraldehyde the smallest sugar molecule also called D-glyceraldehyde in the stereochemical nomenclature used for sugars. Given a Fischer projectionof a monosaccharide classify it by the number of carbons it contains.
Use the Fischer projection shown below for the sugar D-sorbose to draw a Haworth projection of the - and - furanose forms of this sugar. Converting Newman to Fischer Projections. This is video 5 of 5 in the Fischer projection tutorial video series.
Use the Fischer projection below to describe the sugar. Click for the entire series along with my practice quiz and cheat sheet. Given a Fischer projectionof a monosaccharide classify it as either aldosesorketoses.
Putting this together in a three-steps process here is a guide you can use in the practice problems below for converting Fischer projection to Haworth and Chair forms. What is the term to describe the. Note the different patterns of the ce-OH bonds on the left and right sides of the Fischer projection for each.
Below are three representations of the open chain form of D-glucose. In Haworth projections the groups on the right side of a Fischer projection are identical to those below the plane of the ring. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam.
In the conventional Fischer projection A in the line structure variation of the Fischer projection. Is galactose a D-sugar or an L-sugar. For example there are sixteen aldohexoses see figure below.
Use the Fischer projection below to describe the sugar. If not in how many places do they differ. From the abbreviated name of the compound Gal b1 4Glc we know that.
The sugar residue 3 from left has C1 C2C3C4 C5 are chiral. Haworth projections are a type of chemical notation that is used to describe sugar rings. The sugar residue 2 from left has C2C3C4 C5 are chiral.
Watch Previous Video. OH H-C-H CO H-C-OH HO-CH HCOH H-CH OH The sugar shown is a ketopentose and is a D enantiomer and has 3 chiral centers and has 2 possible stereoisomers. Fischer projections provide an easy way to distinguish among the many similar carbohydrate molecules that exist.
Below are two different representations of R-glyceraldehyde the smallest sugar molecule also called D-glyceraldehyde in the stereochemical nomenclature used for sugars. Start studying the Biochem test 3 flashcards containing study terms like Below is the open-chain structure of the monosaccharide D-tagatose which is a ketohexose. Which of the statements below correctly describe the hydrolysis of a carbohydrate.
Draw the Fischer projections for D-galactose and D-fructose. A Haworth projection differs from a Fischer projection in that it is used to represent the carbohydrate in. Chapter 11 Educational Goals 1.
View the full answer. Identify all the functional groups in each structure. Watch How to Use Your Organic Chemistry Model Kit.
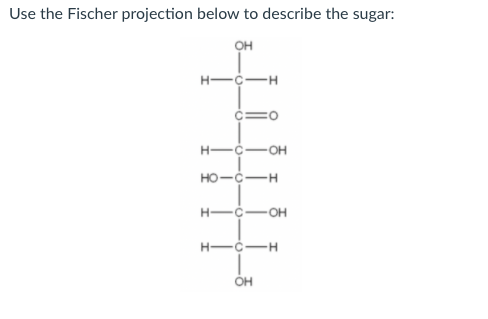
They were initially proposed by Emil Fischer for making it easier to draw the structures of compounds containing multiple chirality centers with the main idea of not having to draw the wedge and dash lines for every single chiral centerThis is especially applicable and used mostly for drawing. In simple terms we can say that it is made up of six carbon atoms twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms. The sugar shown is a ____ and is a ____ enantiomer and has ____ chiral centers and has ____ possible stereoisomers.
For a D-sugar any group that is written to the right of the carbon in a Fischer projection A. A C-4 of glucose is joined to C-1 of galactose by a glycosidic bond. Glucose is a widely available monosaccharide and is also known as dextrose and blood sugar.
B the compound is a D-enantiomer. Given a Fischer projectionof a monosaccharide identify chiral. The fischer projection and the Haworth projection are both used to show carbohydrate stereochemistry.
01 Study the following Fischer projections to answer the questions below. Numbered carbon in the Fischer projection. In the conventional Fischer projection A in the line structure variation of the Fischer projection in which carbons and.
Below are three representations of the open chain form of D-glucose. Furanose Ring Formation Just like we have seen the formation of pyranose rings many monosaccharides typically ketoses tend to also form five-membered rings classified as. The two names describe the same molecule which also happens to be a meso compound because it contains a plane of symmetry.
Fischer projections are just another way of drawing compounds contacting chirality centers. D the glucose is in its pyranose form. Like most monosaccharides it has more than one chiral carbon.
Identify all the functional groups in each structure. Select all of the chiral carbon atoms How many chiral carbon atoms. C the galactose residue is at the reducing end.
Use the Fischer projection shown below for the sugar D-sorbose to draw a Haworth projection of the - and - furanose forms of this sugar. Use the figure of the disaccharide above to decide if it is a reducing or non-reducing sugar. Would a Model Kit help you.
L-Fucose is an aldohexose that is often incorporated into oligosaccharides attached to cell membranes.
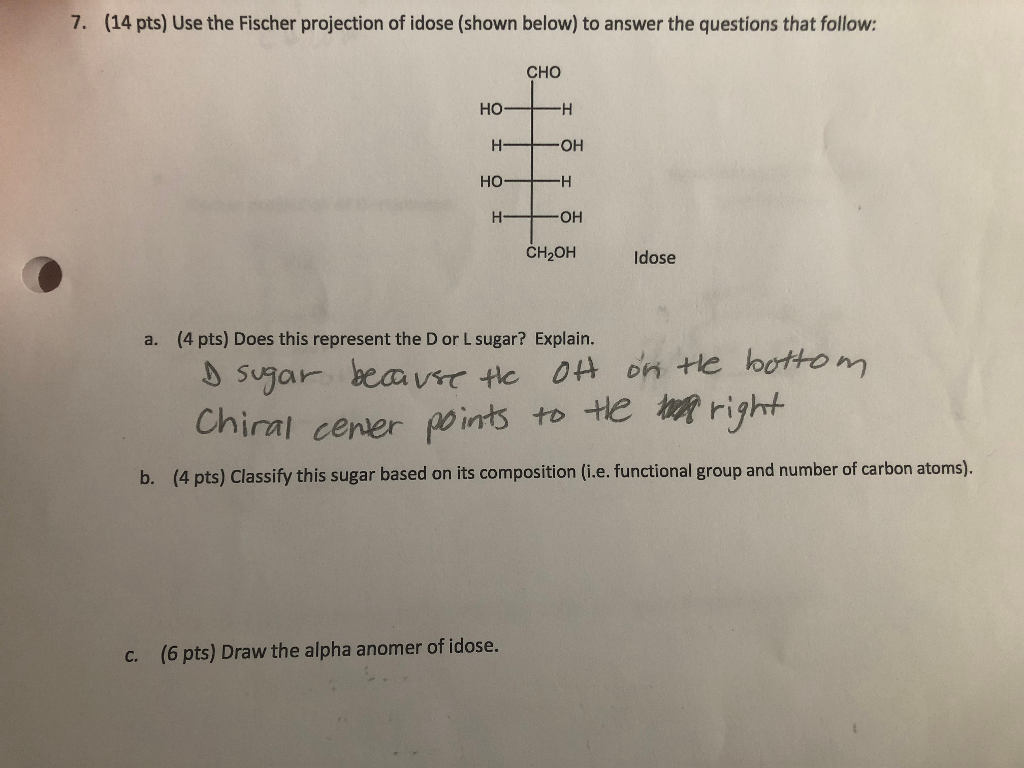
Solved 7 14 Pts Use The Fischer Projection Of Idose Chegg Com

Solved Use The Fischer Projection Below To Describe The Chegg Com
0 Comments